Comparing Left and Right Branch of a Complete Binary Tree
- 时间:2020-09-20 14:08:18
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:112 次
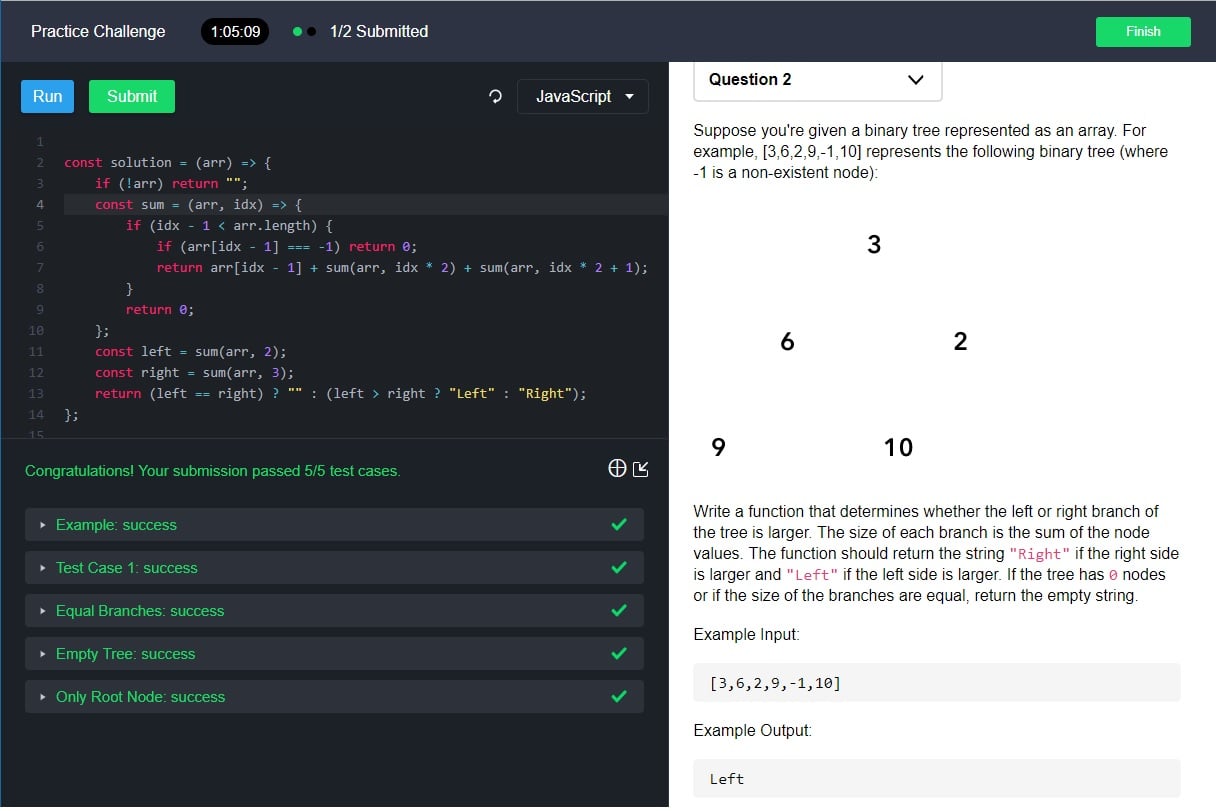
A complete binary tree is a binary tree that each level except possibiliy the last level, is completed filled. Suppose you are giving a binary tree represented as an array. For example, [3, 6, 2, 9, -1, 10] retpresents the following binary tree, where -1 indicates it is a NULL node.
3 6 2 9 10
Write a function that determines whether the left or right branch of the tree is larger. The size of each branch is the sum of the node vlaues. The function should return the string “Right” if the right side is larger and “Left” if the left side is larger. If the tree has zero nodes or if the size of the branches are equal, an empty string “” should be returned.
How to Store/Index a Complete Binary Tree?
We can use an array to index/store a complete binary tree where the root index starts at ONE, and the left child index is always twice its parent index, and the right index is the twice parent index plus one.
For example, in above complete binary tree, the Node 6 has index 2 which is equal to 2*ROOT = 2 * 1. and the Node 2 is 2*ROOT+1 = 2*1+1 = 3.
In the following Javascript method, we have inlined local recursive method that takes the array (complete binary tree) and a node index, which will recursively sum up the nodes in the branch until it gets to the leave nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | const solution = (arr) => { if (!arr) return ""; if (arr.length === 0) return ""; const sum = (arr, idx) => { if (idx - 1 < arr.length) { if (arr[idx - 1] === -1) return 0; return arr[idx - 1] + sum(arr, idx * 2) + sum(arr, idx * 2 + 1); } return 0; }; const left = sum(arr, 2); const right = sum(arr, 3); return (left == right) ? "" : (left > right ? "Left" : "Right"); }; |
const solution = (arr) => {
if (!arr) return "";
if (arr.length === 0) return "";
const sum = (arr, idx) => {
if (idx - 1 < arr.length) {
if (arr[idx - 1] === -1) return 0;
return arr[idx - 1] + sum(arr, idx * 2) + sum(arr, idx * 2 + 1);
}
return 0;
};
const left = sum(arr, 2);
const right = sum(arr, 3);
return (left == right) ? "" : (left > right ? "Left" : "Right");
};Then we can simply call the function twice to compute the sum for left and right branch respectively. The time complexity is O(N) where N is the number of the nodes in the complete binary tree. And the space complexity is O(logN) because the recursion implies a call stack, and the depth for a complete binary tree is O(logN).
binary-tree-left-sum-or-right-sum-larger
You can practice this problem at Hired.com which is a nice career platform for programmers.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:饮食健康与胃病食疗(三):这样饮食降低胃癌风险 冬至时节,常吃这几种传统美食可补阳、防寒! 只有这样吃大蒜才能杀菌防癌,以前你吃对了吗 丝瓜营养丰富,其对人体的保健功效如此之多 患有胃病的人常吃这些食物,可以帮助调理好胃 山药营养丰富食疗价值高,助爱美女性吃出好身材 糖尿病患者常有这些饮食误区,朋友们注意啦! 网络上流传甚广的垃圾食品方便面有毒、致癌的传闻是真的吗? 经常吃核桃仁可以补脑是真的吗 一天吃多少核桃才健康 甘蓝汁食疗方法对胃病患者非常有益 疗效甚至超过单纯药物
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论