How to Compute the Interval List Intersections using Two Pointer
- 时间:2020-09-16 12:48:17
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:106 次
Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order. Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
merge-intervals
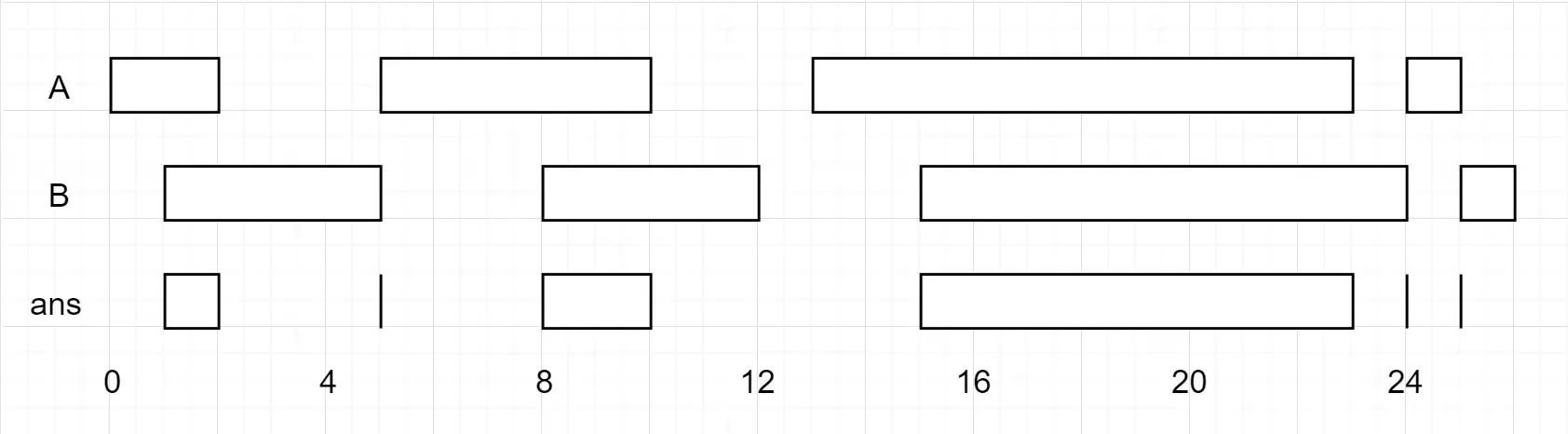
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.Note:
0 <= A.length < 1000
0 <= B.length < 1000
0 <= A[i].start, A[i].end, B[i].start, B[i].end < 10^9
NOTE: input types have been changed on April 15, 2019. Please reset to default code definition to get new method signature.
Merge Intervals using Two Pointers
Since the intervals are sorted, we can have two pointers iteratedly incrementing at two sides. There are 3 pairs (6 circumstances) regarding the relations between interval A and B. We then can deal with them accordingly.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) { vector<vector<int>> r; int n = A.size(); int m = B.size(); int i = 0, j = 0; while ((i < n) && (j < m)) { if (A[i][1] < B[j][0]) { i ++; continue; } if (B[j][1] < A[i][0]) { j ++; continue; } if ((A[i][0] >= B[j][0]) && (A[i][1] <= B[j][1])) { r.push_back(A[i]); i ++; continue; } if ((B[j][0] >= A[i][0]) && (B[j][1] <= A[i][1])) { r.push_back(B[j]); j ++; continue; } if ((A[i][0] <= B[j][0]) && (A[i][1] <= B[j][1])) { r.push_back({B[j][0], A[i][1]}); i ++; continue; } if ((B[j][0] <= A[i][0]) && (B[j][1] <= A[i][1])) { r.push_back({A[i][0], B[j][1]}); j ++; continue; } } return r; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) {
vector<vector<int>> r;
int n = A.size();
int m = B.size();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while ((i < n) && (j < m)) {
if (A[i][1] < B[j][0]) {
i ++;
continue;
}
if (B[j][1] < A[i][0]) {
j ++;
continue;
}
if ((A[i][0] >= B[j][0]) && (A[i][1] <= B[j][1])) {
r.push_back(A[i]);
i ++;
continue;
}
if ((B[j][0] >= A[i][0]) && (B[j][1] <= A[i][1])) {
r.push_back(B[j]);
j ++;
continue;
}
if ((A[i][0] <= B[j][0]) && (A[i][1] <= B[j][1])) {
r.push_back({B[j][0], A[i][1]});
i ++;
continue;
}
if ((B[j][0] <= A[i][0]) && (B[j][1] <= A[i][1])) {
r.push_back({A[i][0], B[j][1]});
j ++;
continue;
}
}
return r;
}
};A and B are either: disjoints, inclusive or interleaving.
It could be improved into the following much more concise solution where we calculate the max of the lower bounds and the min of the higher bounds. Then, the interval is pushed if it is valid.
Then we increment the pointer of the interval where it has a smaller upperbound.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) { vector<vector<int>> r; int n = A.size(); int m = B.size(); int i = 0, j = 0; while ((i < n) && (j < m)) { int start = max(A[i][0], B[j][0]); int end = min(A[i][1], B[j][1]); if (start <= end) { r.push_back({start, end}); } if (A[i][1] < B[j][1]) { i ++; } else { j ++; } } return r; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) {
vector<vector<int>> r;
int n = A.size();
int m = B.size();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while ((i < n) && (j < m)) {
int start = max(A[i][0], B[j][0]);
int end = min(A[i][1], B[j][1]);
if (start <= end) {
r.push_back({start, end});
}
if (A[i][1] < B[j][1]) {
i ++;
} else {
j ++;
}
}
return r;
}
};Both solutions run in O(M + N) time, and require O(1) constant space (excluding the result vector).
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:Exploring the Importance of Brand Consistency Cleaning A WordPress Malware Infection For Dummies 7 Killer Ways to Higher Average Time on Page 6 Tips for Creating Infographics to Make Your Blog Stand Out 11 Foolproof Hacks to Drive Traffic to Your Blog in 2019 7 Things Gutenberg Block Editor Does Better Than The Classic Edi Top 6 Things to Keep in Mind While Sending Bulk Emails 7 Tweaks to Amplify Your Landing Page’s Conversion Rate Fresh Ideas to Make Money Via Your Blog 4 Tips for Earning the Best Quality Backlinks
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论