How many different ways can £2 be made using any number of coins
- 时间:2020-09-10 12:45:51
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:140 次
In the United Kingdom the currency is made up of pound (£) and pence (p). There are eight coins in general circulation:
1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, 50p, £1 (100p), and £2 (200p).
It is possible to make £2 in the following way:
1×£1 + 1×50p + 2×20p + 1×5p + 1×2p + 3×1pHow many different ways can £2 be made using any number of coins?
Depth First Search Algorithm
Let’s define a function f takes two parameters (amount and last). Thus, we can perform a Depth First Search (DFS) search based on the following
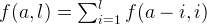
The f(0, x) is 1. We avoid duplicate solution by limiting the current coin strictly less or equal than the last coin.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | function dfs(amount, last) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins if (amount- x >= 0 && x <= last) { // non-bigger ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs } } return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 200)); |
function dfs(amount, last) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins
if (amount- x >= 0 && x <= last) { // non-bigger
ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs
}
}
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 200));The answer is 73682. We can also place a non-less coin and we need to call initially with last equal to 0:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | function dfs(amount, last) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins if (amount- x >= 0 && x >= last) { // non-smaller ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs } } return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 0)); |
function dfs(amount, last) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins
if (amount- x >= 0 && x >= last) { // non-smaller
ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs
}
}
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 0));Counting Number of Coins using Dynamic Programming Algorithm
We notice that we can save the intermediate results so that we don’t respawn too many recursions. The easiest way is to pass a dictionary (or hash map) as a last parameter.
The following Javascript code implements the Dynamic Programming Algorithm to count the coins based on the Recursive Depth First Search with Memoization Technique.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | function dfs(amount, last, cached = {}) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; // if it has been calculated, then return it if (typeof cached[amount + "-" + last] !== "undefined") { return cached[amount+ "-" + last]; } let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { if (amount - x >= 0 && x >= last) { ans += dfs(amount- x, x, cached); } } // save the result in the memo cached[amount+ "-" + last] = ans; return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 0)); |
function dfs(amount, last, cached = {}) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
// if it has been calculated, then return it
if (typeof cached[amount + "-" + last] !== "undefined") {
return cached[amount+ "-" + last];
}
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) {
if (amount - x >= 0 && x >= last) {
ans += dfs(amount- x, x, cached);
}
}
// save the result in the memo
cached[amount+ "-" + last] = ans;
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 0));We can slightly rewrite this, using iterative approach. We sort the coins and start from the smallest coin. For each coin, we then incrementally update the answer.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | function dp(amount) { let f = Array(amount + 1).fill(0); f[0] = 1; for (let x of [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]) { for (let a = x; a <= amount; ++ a) { f[a] += f[a - x]; } } return f[amount]; } |
function dp(amount) {
let f = Array(amount + 1).fill(0);
f[0] = 1;
for (let x of [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]) {
for (let a = x; a <= amount; ++ a) {
f[a] += f[a - x];
}
}
return f[amount];
}The algorithmic complexity is O(NM) where N is the number of the coin-types and M is the amount. The space complexity is O(M).
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:平年和闰年自测题 数学题:李爷爷家住在半山腰 数学题:无线电元件厂验收一批零件 数学题:调查发现,该学校七年级参加魔方比赛的学生中 数学题:甲乙两辆客车同时从东站开往西站 数学题:养猪大户王师傅说他的猪卖75头 数学题:下图是一个正方形,边长是6厘米 数学题:求往返的平均速度 同学,很高兴认识你们 我想让校园更美
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论