How to Clone a Graph in C++/Java using Depth First Search Algori
- 时间:2020-10-11 15:48:46
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:137 次
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph, return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
clone-graph-algorithm
Input:
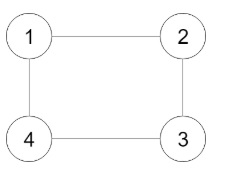
{"$id":"1","neighbors":[{"$id":"2","neighbors":[{"$ref":"1"},{"$id":"3","neighbors":[{"$ref":"2"},{"$id":"4","neighbors":[{"$ref":"3"},{"$ref":"1"}],"val":4}],"val":3}],"val":2},{"$ref":"4"}],"val":1}Explanation:
- Node 1’s value is 1, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
- Node 2’s value is 2, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
- Node 3’s value is 3, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
- Node 4’s value is 4, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Note:
- The number of nodes will be between 1 and 100.
- The undirected graph is a simple graph, which means no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- Since the graph is undirected, if node p has node q as neighbor, then node q must have node p as neighbor too.
- You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
C++ Algorithm to Clone a Unidirectional Graph
Since the graph is unidirectional, it can also be seen as bi-directional. A’s neighbors contain B and B’s neighours contain also A. By using DFS (Depth First Search), we have to solve the loop problem – which is to avoid cloning the same node again and again.
The solution is easy: to use the hash map, that remembers the mappings between source nodes and the cloned nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> neighbors; Node() {} Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) { if (node == NULL) return NULL; if (copied.find(node) != copied.end()) { // already cloned return copied[node]; } vector<Node*> nbs = {}; Node* root = new Node(node->val, nbs); copied[node] = root; // mark it cloned first to avoid stack overflow. for (const auto &n: node->neighbors) { root->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(n)); // clone the neighboured recursively } return root; } private: unordered_map<Node*, Node*> copied; }; |
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> neighbors;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return NULL;
if (copied.find(node) != copied.end()) { // already cloned
return copied[node];
}
vector<Node*> nbs = {};
Node* root = new Node(node->val, nbs);
copied[node] = root; // mark it cloned first to avoid stack overflow.
for (const auto &n: node->neighbors) {
root->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(n)); // clone the neighboured recursively
}
return root;
}
private:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> copied;
};The above C++ algorithm to clone graphs take O(N) complexity in both time and space where N is the number of nodes in the graph.
Java Recursive Algorithm (DFS) to clone graph
Same algorithm (in recursion) can be implemented in Java as follows. The neighbour nodes are cloned by using Depth First Search recursion.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,List<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } }; */ class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (copied.containsKey(node)) { // graph node cloned already return copied.get(node); } Node root = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<Node>()); copied.put(node, root); // mark it cloned to avoid duplication for (Node n: node.neighbors) { root.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(n)); // clone the neighbours recursively } return root; } private HashMap<Node, Node> copied = new HashMap<>(); } |
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,List<Node> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (copied.containsKey(node)) { // graph node cloned already
return copied.get(node);
}
Node root = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<Node>());
copied.put(node, root); // mark it cloned to avoid duplication
for (Node n: node.neighbors) {
root.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(n)); // clone the neighbours recursively
}
return root;
}
private HashMap<Node, Node> copied = new HashMap<>();
}Similarly, we can use such algorithms to clone (deep copy) a binary tree: Clone (Deep Copy) Binary Tree With Random Pointer using Hash Map and Recursion
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:巧用wordpress更新服务 提升搜索引擎收录文章的速度 无需登陆FTP 新建一个wordpress主题文件 wordpress响应式杂志主题—Semicolon 禁止wordpress仪表盘加载谷歌字体链接 通过wordpress仪表盘修改wp_options数据表 荆州古城作文400字 过程胜过结局作文800字 新之三下乡第一天 过三八妇女节有感300字 吹鸡毛作文300字
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论