How to Compute the Projection Area of 3D Shapes?
- 时间:2020-10-06 11:32:45
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:106 次
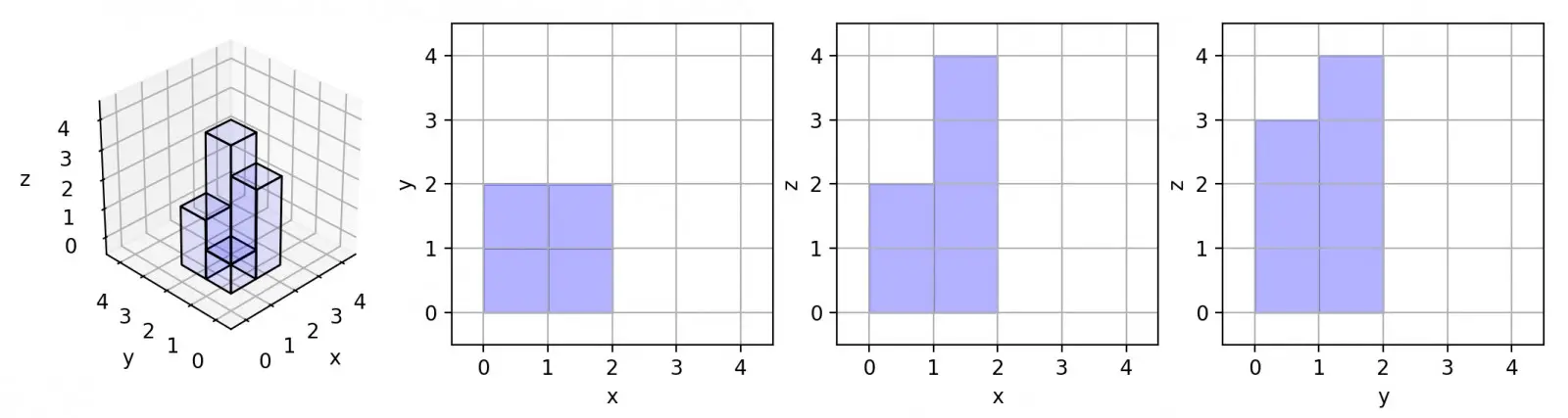
On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes. Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j). Now we view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes. A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3 dimensional figure to a 2 dimensional plane. Here, we are viewing the “shadow” when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side. Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
Input: [[2]]
Output: 5Example 2:
Input: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation:
Here are the three projections (“shadows”) of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.cubes-in-3d-axies
Example 3:
Input: [[1,0],[0,2]]
Output: 8Example 4:
Input: [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 14Example 5:
Input: [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
Output: 21Note:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 50
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
Projection Area of 3D Shapes
This problem may seem hard, but it is actually easy to solve. The X-Y view area can be counted by the non-zero cubes, which is the the input array. Then, Y-Z view will be the sum of the maximum of each row and similary X-Z view will be the sum of the maximum for each column.
The maximum for each rows are easy to compute and stored as we iterate the array. The column maxs can be done similarly via another O(N) loop where N is the number of the input cubes. However, it will be slightly faster if we use a hash map e.g. unordered_map in C++, to remember/update the column maxs.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | class Solution { public: int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int ans = 0; unordered_map<int, int> columns; for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); ++ i) { int rowMax = 0; for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].size(); ++ j) { if (grid[i][j] != 0) ans ++; // xy rowMax = max(grid[i][j], rowMax); if (columns.find(j) == columns.end()) { columns[j] = grid[i][j]; } else { columns[j] = max(columns[j], grid[i][j]); } } ans += rowMax; // yz } for (auto &it: columns) { ans += it.second; // xz } return ans; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int ans = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> columns;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); ++ i) {
int rowMax = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].size(); ++ j) {
if (grid[i][j] != 0) ans ++; // xy
rowMax = max(grid[i][j], rowMax);
if (columns.find(j) == columns.end()) {
columns[j] = grid[i][j];
} else {
columns[j] = max(columns[j], grid[i][j]);
}
}
ans += rowMax; // yz
}
for (auto &it: columns) {
ans += it.second; // xz
}
return ans;
}
};The overall complexity is O(N) time and O(N) space – consider the input can be just a row of cubes.
Similar post: How to Compute the Surface Area of 3D Shapes (Cubes Placed on Grid Cells)?
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:4 Tech Trends You Need To Get Prepared For Blogger Sentenced To Two Years In Prison After Insulting Preside Back to Basics: Blogging and Copyright Infringement How To Jazz Up That Boring Business Blog The Life Of A Million-Dollar Blogger 5 Types of Stories You Can Tell About Your Business The Maximum Average Subtree of a Binary Tree How to Design a Snake Game? How to Design a Two-Sum Data Structure? The MySQL If and Case Statement Exercise: How to Swap Elements i
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论