The Beginners’ Guide to Trie: How to Use the Trie in C++?
- 时间:2020-09-23 15:50:46
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:118 次
The Trie is common used data structure to speed up the word searching. The Trie is a structure to index the words character by character.
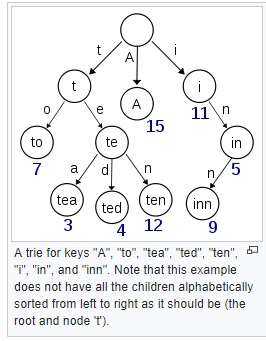
trie-example
Trie Definition in C++
Take a lowercase 26 letters for example, we can define a Trie node as a struct, as the follows:
1 2 3 4 5 | struct TrieNode { TrieNode* children[26] = { nullptr }; bool isWord = false; // denote if up to this point a word is complete string word = ""; // optional }; |
struct TrieNode {
TrieNode* children[26] = { nullptr };
bool isWord = false; // denote if up to this point a word is complete
string word = ""; // optional
};Of course, you can define it as a class, but a Struct is lightweight, and serve the purpose. Each TrieNode will have an array of pointers indicating its next character. Meantime, it will have a boolean field to denote weather current node is the end of a word.
Insert/Index a Word in the Trie
First, we can declare a root node, then, we can call the following functoin to insert/index a word in the Trie.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | void insert(struct TrieNode* root, string key) { struct TrieNode *p = root; for (const auto &n: key) { int index = n - 'a'; if (p->children[index] == nullptr) { // not found, create a new child node p->children[index] = new TrieNode(); } // navigate the Trie Path p = p->children[index]; } // reaching the end of the word, mark it complete p->isWord = true; p->word = key; } |
void insert(struct TrieNode* root, string key) {
struct TrieNode *p = root;
for (const auto &n: key) {
int index = n - 'a';
if (p->children[index] == nullptr) {
// not found, create a new child node
p->children[index] = new TrieNode();
}
// navigate the Trie Path
p = p->children[index];
}
// reaching the end of the word, mark it complete
p->isWord = true;
p->word = key;
}The indexing takes O(N) for inserting a word to the dictionary where N is the length of the word string.
Search a Word in the Trie
Given a root of TrieNode, we can easily follow the path until it has reached the end of the word i.e. the TrieNode’s isWord is true or NULL which indicates that the word is not in the dictionary.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | bool search(struct TrieNode* root, string key) { struct TrieNode *p = root; for (const auto &n: key) { int index = n - 'a'; // not found in the dictionary if (p->children[index] == nullptr) return false; // navigate to next letter p = p->children[index]; } // the current node is the end of the word return (p != nullptr) && (p->isWord); } |
bool search(struct TrieNode* root, string key) {
struct TrieNode *p = root;
for (const auto &n: key) {
int index = n - 'a';
// not found in the dictionary
if (p->children[index] == nullptr) return false;
// navigate to next letter
p = p->children[index];
}
// the current node is the end of the word
return (p != nullptr) && (p->isWord);
}Finding a word is O(N) where N is the number of the characters.
Example of Using Trie
1 2 3 4 | struct TrieNode *root = new TrieNode(); insert(root, "hello world!"); search(root, "hello"); // false search(root, "hello world!"); // true |
struct TrieNode *root = new TrieNode(); insert(root, "hello world!"); search(root, "hello"); // false search(root, "hello world!"); // true
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:长方体和正方体思维导图 一个整数除以小数是什么含义? 平行四边形、梯形、三角形的高一定要画成虚线吗? 格子乘法介绍 两个因数的末尾一共有几个零,积的末尾就有几个零。 四边形整理和复习思维导图 一些常见数的倍数的特征 什么是集合? 为什么要先乘除后加减 球的体积公式推导证明
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论