Beginner’s Guide to the zip() function in Python3
- 时间:2020-09-21 09:15:21
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:118 次
The zip function in Python 3 takes two parameters, and generate an iterator that contains tuples. Each tuple takes a value from each input – which can be tuples or arrays. It can be illustrated as follows:
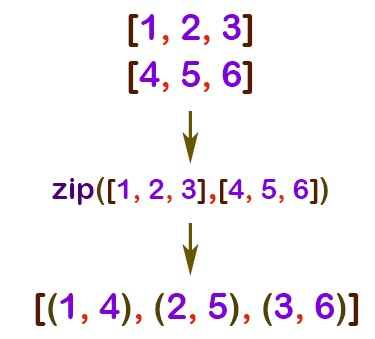
python3-zip-function
Python3 zipping two tuples
In Python2, the zip function will return all the zipped-elements in an array while in Python3, the zip function will returns an iterator – saving memory. For example,
1 2 3 4 | a = (1, 2, 3) b = (4, 5, 6) zip(a, b) # <zip object at 0x7ff81cb770c8> list(zip(a, b)) # [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)] |
a = (1, 2, 3) b = (4, 5, 6) zip(a, b) # <zip object at 0x7ff81cb770c8> list(zip(a, b)) # [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)]
As you can see in this example, the source inputs can be tuples as well. You can mix-and-match and the result is always an iterator. Then you can easily convert the iterator to array using list() or to set using the set().
zipping takes minimal length
If both inputs are of different sizes, the zip function will only zip the minimal length of both. For example,
1 2 3 4 | a = (1, 2, 3, 4) b = (4, 5, 6) zip(a, b) # <zip object at 0x7abcdcb770c8> set(zip(a, b)) # {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} |
a = (1, 2, 3, 4)
b = (4, 5, 6)
zip(a, b) # <zip object at 0x7abcdcb770c8>
set(zip(a, b)) # {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)}zip nested elements
The zip function can take nested inputs as well, for example:
1 2 3 | a=[(1,2),(3,4)] b=[(5,6),(7,8)] list(zip(a,b)) # produces [((1, 2), (5, 6)), ((3, 4), (7, 8))] |
a=[(1,2),(3,4)] b=[(5,6),(7,8)] list(zip(a,b)) # produces [((1, 2), (5, 6)), ((3, 4), (7, 8))]
You can use the zip() function to achieve something similar of what the enumerate() does in Python.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:滕王阁序原文及翻译 谏太宗十思疏原文及翻译 红梅本来有几粒糖 摸黄球白球可能性的问题 如果要准时到达需要多少小时 货物的原价是多少元 用去水泥和沙子各多少吨 求AB两站距离的问题 如图小正方形的边长为5cm求阴影部分的面积 全天计划生产消毒药水多少瓶
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论