Linear Algorithm to Check If All 1’s Are at Least Length K
- 时间:2020-09-09 14:04:20
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:135 次
Given an array nums of 0s and 1s and an integer k, return True if all 1’s are at least k places away from each other, otherwise return False.
Example 1:
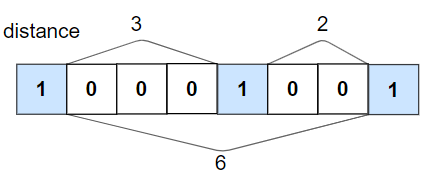
Input: nums = [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], k = 2
Output: true
Explanation: Each of the 1s are at least 2 places away from each other.
Example 2:
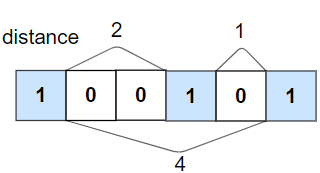
Input: nums = [1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 2
Output: false
Explanation: The second 1 and third 1 are only one apart from each other.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1], k = 0
Output: trueExample 4:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,1], k = 1
Output: trueConstraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
0 <= k <= nums.length
nums[i] is 0 or 1Hints:
Each time you find a number 1, check whether or not it is K or more places away from the next one. If it’s not, return false.
Check If All 1’s Are at Least Length K Places Away
We remember and update the last position of the 1’s if we go through the binary array one by one. And return false if we found current is one and the distance is more than K places away than the last one. If it reaches the end, then we simply return true.
The complexity is O(N) linear as we are iterating the array once.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class Solution { public: bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) { int last = -1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) { if (nums[i] == 1) { if (last != -1) { if (i - last - 1 < k) return false; } last = i; } } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
if (last != -1) {
if (i - last - 1 < k) return false;
}
last = i;
}
}
return true;
}
};Note that we may not need to check if the flag is negative (which is intialised to negative one). Instead, we can initialise the last position to (-k-1).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | class Solution { public: bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) { int last = -k - 1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) { if (nums[i] == 1) { if (i - last - 1 < k) return false; last = i; } } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int last = -k - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
if (i - last - 1 < k) return false;
last = i;
}
}
return true;
}
};This is a much cleaner implementation of the same algorithm.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:微笑送给你我她(他)——读文章《感谢近视》有感450字 聪明的公鸡作文150字 狂欢是一群人的寂寞,独处是一个人的狂欢 家乡的明天_小学生六一作文 简单的文明作文900字 咿咿呀呀发表了日志当下雪遇到阳光 一场春雨作文 历史上的遗憾——读《圆明园的毁灭》有感 诗词名句鉴赏:一日不见,如三秋兮! 宫之奇谏假道原文及翻译
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论