Algorithm to Check if All Points are On the Same Line
- 时间:2020-09-09 13:16:32
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:128 次
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
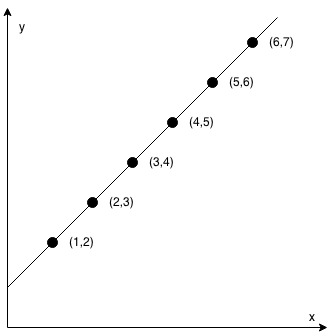
Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
Output: true
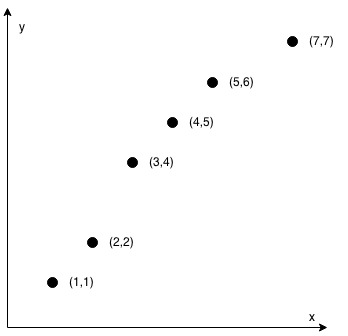
Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
Output: false
Constraints:
2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000
coordinates[i].length == 2
-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4
coordinates contains no duplicate point.Hints:
If there’re only 2 points, return true.
Check if all other points lie on the line defined by the first 2 points.
Use cross product to check collinearity.
Cross Product to Check If Points are On a Line
If there are less than or equal to two points, we return true – as 1 or 2 points must be on the line. Then we use the first two points to compute the delta x and y offsets. Then checking from the third point, we can use the cross product to see if it is the same.
The following C++ implementation has O(N) linear runtime complexity.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | class Solution { public: bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) { if (coordinates.size() <= 2) return true; int dx = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[1][0]; int dy = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[1][1]; for (int i = 2; i < coordinates.size(); ++ i) { int dx1 = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[i][0]; int dy1 = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[i][1]; if (dx1 * dy != dy1 * dx) return false; } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) {
if (coordinates.size() <= 2) return true;
int dx = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[1][0];
int dy = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[1][1];
for (int i = 2; i < coordinates.size(); ++ i) {
int dx1 = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[i][0];
int dy1 = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[i][1];
if (dx1 * dy != dy1 * dx) return false;
}
return true;
}
};The cross product (one of the most classic geometrygeometry algorithms) returns the perpendicular vector/line to the original line. If the cross product is the same, then the point must be on the same line.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:饮食安全:隔夜食物危害到底有多大? 市场上的“非油炸”食品真没油吗 包装上宣称“无糖”的食品真没糖吗 号称“零脂肪”的乳品同样会引发肥胖 宣称“高钙”的食品补钙效果未必好 广告中的“高膳食纤维”食品并不健康 宣传的“零热量”饮品真的很不靠谱 宣称健康的“全谷物”饮品营养仅一般 国家食品药品监督管理总局正式挂牌 办公室白领防电脑辐射食品大盘点
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论