Powerful Integers by Bruteforce Algorithm using C++
- 时间:2020-09-27 14:36:16
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:144 次
Given two positive integers x and y, an integer is powerful if it is equal to x^i + y^j for some integers i >= 0 and j >= 0. Return a list of all powerful integers that have value less than or equal to bound. You may return the answer in any order. In your answer, each value should occur at most once.
Example 1:
Input: x = 2, y = 3, bound = 10
Output: [2,3,4,5,7,9,10]Explanation:
2 = 2^0 + 3^0
3 = 2^1 + 3^0
4 = 2^0 + 3^1
5 = 2^1 + 3^1
7 = 2^2 + 3^1
9 = 2^3 + 3^0
10 = 2^0 + 3^2Example 2:
Input: x = 3, y = 5, bound = 15
Output: [2,4,6,8,10,14]Note:
1 <= x <= 100
1 <= y <= 100
0 <= bound <= 10^6
C++ Bruteforce Algorithm to Compute the Powerful Integers
The edge cases are when x and y are equal to 1. We can use a set to store the unique powerful integers within the bound. If X = 1 or Y = 1, the time complexity is 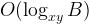 . If both are 1, then the complexity is O(1) – as there is only 1 powerful integer, which is 1+1=2.
. If both are 1, then the complexity is O(1) – as there is only 1 powerful integer, which is 1+1=2.
If neither X or Y is 1, the time complexity is 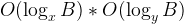 . The space complexity is the same the time complexity as each number to test may be a potential powerful integer.
. The space complexity is the same the time complexity as each number to test may be a potential powerful integer.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | class Solution { public: vector<int> powerfulIntegers(int x, int y, int bound) { unordered_set<int> data; int a, b; for (int i = 0; (a = pow(x, i)) <= bound; ++ i) { for (int j = 0; (b = a + pow(y, j)) <= bound; ++ j) { if (b <= bound) { data.insert(b); } else break; if (y == 1) break; } if (x == 1) break; } vector<int> res; std::copy(data.begin(), data.end(), std::back_inserter(res)); return res; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> powerfulIntegers(int x, int y, int bound) {
unordered_set<int> data;
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; (a = pow(x, i)) <= bound; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0; (b = a + pow(y, j)) <= bound; ++ j) {
if (b <= bound) {
data.insert(b);
} else break;
if (y == 1) break;
}
if (x == 1) break;
}
vector<int> res;
std::copy(data.begin(), data.end(), std::back_inserter(res));
return res;
}
};And, if either X or Y is 1, we can break the loop – as 1 to the power of any will be still one, otherwise, it will be an endless loop. At last, we need to convert the set to std::vector in C++ and in this post, there are quite a few methods to do that.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:Keyword Rank Tracking: What Newbie Bloggers Need to Know Why Digital Products are the Key to Success for Bloggers Why You Should Consider Alternative Domain Name Extensions for y How to Create a Successful WordPress Site How to Launch an E-Course the Right Way as a Blogger Is Malaysia finally cleaning up corruption? I think not. How to use ‘Answer the Public’ to Create Unmissable Blog Posts A Guide to Handling Negative Comments and Reviews The Best Link Building Methods For Your Website How To Use Twitter To Get New Clients
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论