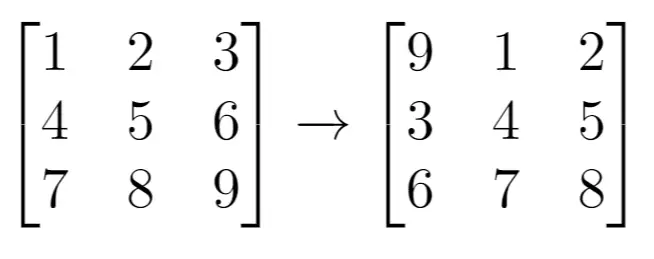Algorithms to Shift a 2D Grid/Matrix In-Place
- 时间:2020-09-17 10:57:36
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:123 次
Given a 2D grid of size n * m and an integer k. You need to shift the grid k times.
In one shift operation:
- Element at grid[i][j] becomes at grid[i][j + 1].
- Element at grid[i][m – 1] becomes at grid[i + 1][0].
- Element at grid[n – 1][m – 1] becomes at grid[0][0].
- Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation k times.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
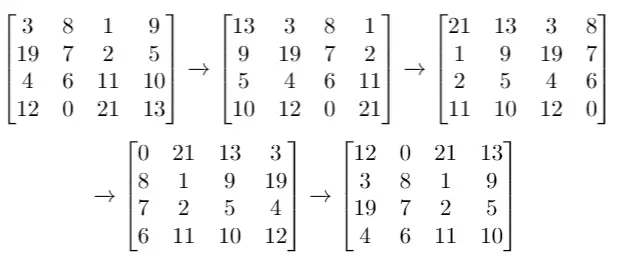
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]Constraints:
1 <= grid.length <= 50
1 <= grid[i].length <= 50
-1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1000
0 <= k <= 100Hints:
Simulate step by step. move grid[i][j] to grid[i][j+1]. handle last column of the grid.
Put the matrix row by row to a vector. take k % vector.length and move last k of the vector to the beginning. put the vector to the matrix back the same way.
How to Shift a 2D Grid/Matrix in 2D?
The last element in the 2D Grid/Matrix needs to be overwritten first, thus value needs to be saved. Then, we can start shifting backwards from the last row, last column. Special cases have to be taken care when dealing with the first element (as it should be set the original last value), and the first columns need to be taking its previous row and last column.
Therefore, many conditions are existen in the loop, which could be unrolled.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) { for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) { int n = grid.size(); int m = grid[0].size(); int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1]; for (int row = n - 1; row >= 0; -- row) { for (int col = m - 1; col >= 0; -- col) { if ((row == 0) && (col == 0)) { // first element grid[0][0] = last; } else { if (col == 0) { // first column grid[row][col] = grid[row - 1][m - 1]; } else { grid[row][col] = grid[row][col - 1]; } } } } } return grid; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1];
for (int row = n - 1; row >= 0; -- row) {
for (int col = m - 1; col >= 0; -- col) {
if ((row == 0) && (col == 0)) { // first element
grid[0][0] = last;
} else {
if (col == 0) { // first column
grid[row][col] = grid[row - 1][m - 1];
} else {
grid[row][col] = grid[row][col - 1];
}
}
}
}
}
return grid;
}
};You could unroll the IF conditions and take care of the first columns, and first row especially.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) { for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) { int n = grid.size(); int m = grid[0].size(); int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1]; for (int row = n - 1; row > 0; -- row) { for (int col = m - 1; col > 0; -- col) { grid[row][col] = grid[row][col - 1]; } grid[row][0] = grid[row - 1][m - 1]; // first column } for (int col = m - 1; col > 0; -- col) { // first row grid[0][col] = grid[0][col - 1]; } grid[0][0] = last; // first element } return grid; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1];
for (int row = n - 1; row > 0; -- row) {
for (int col = m - 1; col > 0; -- col) {
grid[row][col] = grid[row][col - 1];
}
grid[row][0] = grid[row - 1][m - 1]; // first column
}
for (int col = m - 1; col > 0; -- col) { // first row
grid[0][col] = grid[0][col - 1];
}
grid[0][0] = last; // first element
}
return grid;
}
};How to Shift a 2D Grid/Matrix in 1D?
We know the total elements are row*column thus, we can loop backwards a single index, then converting to row and column indices. This helps to make a single loop concise. The first element needs to be handled (special case).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) { for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) { int n = grid.size(); int m = grid[0].size(); int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1]; for (int i = m * n - 1; i > 0; -- i) { int row = i / m; int col = i % m; int row1 = (i - 1) / m; int col1 = (i - 1) % m; grid[row][col] = grid[row1][col1]; } grid[0][0] = last; } return grid; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> shiftGrid(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++ i) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
int last = grid[n - 1][m - 1];
for (int i = m * n - 1; i > 0; -- i) {
int row = i / m;
int col = i % m;
int row1 = (i - 1) / m;
int col1 = (i - 1) % m;
grid[row][col] = grid[row1][col1];
}
grid[0][0] = last;
}
return grid;
}
};All above C++ implementations are O(RC) time where R is the row number and C is the number of the columns for the 2D Grid. Alternatively, we can say it is O(N) where N is the number of elements in the 2D Grid/Matrix. The space requirement is O(1) constant as we are shifting the 2D array/matrix in place without allocating extra arrays.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:留意幸福角 钉扣子作文400字 清明随感作文 论威严的重要性 拥有一颗周全的心作文 我们一起来向笑猫学习——《笑猫日记》读后感 相亲 描写校园春色的作文 钉扣子作文200字 由大山和卵石的对话想起的作文500字
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论