Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm to Compute the Sum of Nod
- 时间:2020-09-12 10:06:27
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:139 次
Given a binary tree, return the sum of values of nodes with even-valued grandparent. (A grandparent of a node is the parent of its parent, if it exists.)
If there are no nodes with an even-valued grandparent, return 0.
binary-tree-grandparent
Example 1:
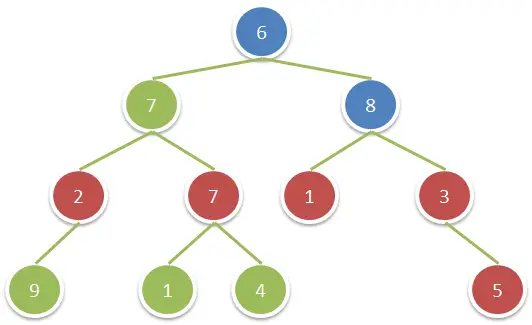
Input: root = [6,7,8,2,7,1,3,9,null,1,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: 18
Explanation: The red nodes are the nodes with even-value grandparent while the blue nodes are the even-value grandparents.Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is between 1 and 10^4.
The value of nodes is between 1 and 100.Hints:
Traverse the tree keeping the parent and the grandparent.
If the grandparent of the current node is even-valued, add the value of this node to the answer.
Depth First Search Algorithm to Pass the Parent and GrandParent Nodes
When we do a DFS (Depth First Search) Algorithm from the root, we can pass down the parent, and the grandparent nodes. Thus, when conditions are met (the grandparent nodes have even values), we accumulate the sum.
The implementation is done via Recursion, and the runtime complexity is O(N) where N is the number of the nodes in the binary tree. The space requirement is also O(N) where the binary tree in worst case may become the singly linked list and the usage of recursion yields the stack-calls.
The C++ code to traverse the binary tree in DFS:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root, nullptr, nullptr); return sum; } private: int sum = 0; void dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* parent, TreeNode* grandparent) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (grandparent != nullptr && grandparent->val % 2 == 0) { sum += root->val; } dfs(root->left, root, parent); dfs(root->right, root, parent); } }; |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, nullptr, nullptr);
return sum;
}
private:
int sum = 0;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* parent, TreeNode* grandparent) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
if (grandparent != nullptr && grandparent->val % 2 == 0) {
sum += root->val;
}
dfs(root->left, root, parent);
dfs(root->right, root, parent);
}
};And here is the Java code to visit the binary tree in DFS:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { private int sum = 0; public int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode root) { dfs(root, null, null); return sum; } private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode parent, TreeNode grandparent) { if (root == null) return; if (grandparent != null && (grandparent.val % 2 == 0)) { sum += root.val; } dfs(root.left, root, parent); dfs(root.right, root, parent); } } |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int sum = 0;
public int sumEvenGrandparent(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, null, null);
return sum;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode parent, TreeNode grandparent) {
if (root == null) return;
if (grandparent != null && (grandparent.val % 2 == 0)) {
sum += root.val;
}
dfs(root.left, root, parent);
dfs(root.right, root, parent);
}
}–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:为wordpress编辑器添加选择中文字体功能 让WordPress编辑器TinyMCE显示隐藏按钮 冬日趣事作文200字 走出来,真好 创新是不变的旋律 中华传统节日重阳节作文400字 怀揣感恩之心 春的脚步作文400字 好习惯让人受益一生 我最喜欢去的一个地方
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论