Using Depth First Search Algorithm to Delete Tree Nodes with Sum
- 时间:2020-09-10 13:27:27
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:120 次
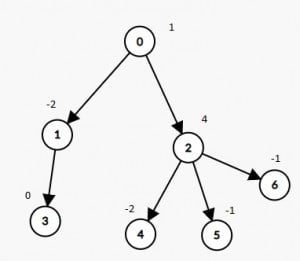
A tree rooted at node 0 is given as follows:
The number of nodes is nodes;
The value of the i-th node is value[i];
The parent of the i-th node is parent[i].
Remove every subtree whose sum of values of nodes is zero.After doing so, return the number of nodes remaining in the tree.
Input: nodes = 7, parent = [-1,0,0,1,2,2,2], value = [1,-2,4,0,-2,-1,-1]
Output: 2binary-tree-delete-nodes-with-zero-sum-sub-tree
Constraints:
1 <= nodes <= 10^4
-10^5 <= value[i] <= 10^5
parent.length == nodes
parent[0] == -1 which indicates that 0 is the root.Hints:
Traverse the tree using depth first search.
Find for every node the sum of values of its sub-tree.
Traverse the tree again from the root and return once you reach a node with zero sum of values in its sub-tree.
How to Delete Nodes from Binary Tree using Depth First Search Algorithm?
The binary tree is given in two arrays, we can convert it using the adjacent graph – two dimension array or vectors. Then we can run a DFS (Depth First Search) algorithm that travels the tree from root to leaves recursively.
Bottom-up, from the leaves, we accumulate the sum and the count of the nodes (remaining). At any point, if the sum is zero, we set the counter to zero – which will be bubbled up as the recursion unrolls.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | class Solution { public: int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& value) { vector<vector<int>> g(nodes, vector<int>(0)); for (int i = 0; i < nodes; ++ i) { if (parent[i] == -1) continue; g[parent[i]].push_back(i); } return dfs(g, 0, value)[1]; } private: vector<int> dfs(const vector<vector<int>> &g, int root, const vector<int>& value) { int sum = value[root]; int remain = 1; for (const auto &child: g[root]) { vector<int> r = dfs(g, child, value); remain += r[1]; sum += r[0]; } if (sum == 0) remain = 0; return {sum, remain}; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& value) {
vector<vector<int>> g(nodes, vector<int>(0));
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; ++ i) {
if (parent[i] == -1) continue;
g[parent[i]].push_back(i);
}
return dfs(g, 0, value)[1];
}
private:
vector<int> dfs(const vector<vector<int>> &g, int root, const vector<int>& value) {
int sum = value[root];
int remain = 1;
for (const auto &child: g[root]) {
vector<int> r = dfs(g, child, value);
remain += r[1];
sum += r[0];
}
if (sum == 0) remain = 0;
return {sum, remain};
}
};The time complexity is O(N) where N is the number of the nodes in the binary tree. The space complexity is also O(N) due to the stack in recursion.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:萤火之光,可以照明 看得破的是人生作文200字 学《弟子规》有感 描写五莲山风景的作文 诗词名句鉴赏:少壮不努力,老大徒伤悲。 诗词名句鉴赏:秋风萧萧愁杀人 诗词名句鉴赏:树欲静而风不止 诗词名句鉴赏:忧艰常早至,欢会常苦晚。 春王正月原文及翻译 诗词名句鉴赏:风萧萧兮易水寒,壮士一去兮不复还!
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论