How to Delete N Nodes After M Nodes of a Linked List?
- 时间:2020-09-08 11:19:41
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:110 次
Given the head of a linked list and two integers m and n. Traverse the linked list and remove some nodes in the following way:
Start with the head as the current node.
Keep the first m nodes starting with the current node.
Remove the next n nodes
Keep repeating steps 2 and 3 until you reach the end of the list.
Return the head of the modified list after removing the mentioned nodes.Follow up question: How can you solve this problem by modifying the list in-place?
delete-n-nodes-after-m-nodes-of-a-linked-list
Example 1:
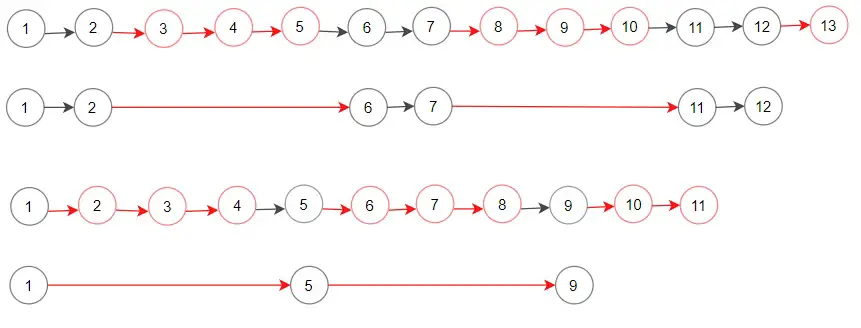
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], m = 2, n = 3
Output: [1,2,6,7,11,12]
Explanation: Keep the first (m = 2) nodes starting from the head of the linked List (1 ->2) show in black nodes.
Delete the next (n = 3) nodes (3 -> 4 -> 5) show in read nodes.
Continue with the same procedure until reaching the tail of the Linked List.
Head of linked list after removing nodes is returned.Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], m = 1, n = 3
Output: [1,5,9]
Explanation: Head of linked list after removing nodes is returned.Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], m = 3, n = 1
Output: [1,2,3,5,6,7,9,10,11]Example 4:
Input: head = [9,3,7,7,9,10,8,2], m = 1, n = 2
Output: [9,7,8]Constraints:
The given linked list will contain between 1 and 10^4 nodes.
The value of each node in the linked list will be in the range [1, 10^6].
1 <= m,n <= 1000Hints:
Traverse the Linked List, each time you need to delete the next n nodes connect the nodes previous deleting with the next node after deleting.
C++ Algorithm to Delete N Nodes After M Nodes of a Linked List in Place
Most linked list problems can be helped by using a dummy header pointer. In this particular problem, we need also a previous pointer. By skipping current M nodes, and we need to link the previous pointer to next pointer – which basically delete N nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteNodes(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* prev = dummy; prev->next = head; while (head != NULL) { for (int i = 0; (i < m) && (head != NULL); ++ i) { prev = head; head = head->next; } for (int i = 0; (i < n) && (head != NULL); ++ i) { head = head->next; } prev->next = head; } return dummy->next; } }; |
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNodes(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* prev = dummy;
prev->next = head;
while (head != NULL) {
for (int i = 0; (i < m) && (head != NULL); ++ i) {
prev = head;
head = head->next;
}
for (int i = 0; (i < n) && (head != NULL); ++ i) {
head = head->next;
}
prev->next = head;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};We also need to take care of the cases when there are less than M nodes to skip. In this case, we would just point previous pointer to NULL.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:5 Helpful Sales Enablement Blogs For Empowering Salespeople How to Plan for Your Financial Future as a Content Marketer Reasons You Should Invest in SEO 7 Reasons Website Maintenance Is Crucial 7 Best Archive Plugins for Your WordPress Blog How to Make Your Blog Accessible to Disabled Users with accessiB 向阳实践队摄影组组长心得 我与篮球有个约会 让你、我、他都成为雷锋吧 理解之花作文550字
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论