Deep Clone N-ary Tree using Hash Map + Recursive Depth First Sea
- 时间:2020-09-08 11:08:55
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:125 次
Given a root of an N-ary tree, return a deep copy (clone) of the tree.
Each node in the n-ary tree contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its children.
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; }Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Follow up: Can your solution work for the graph problem?
n-ary-tree
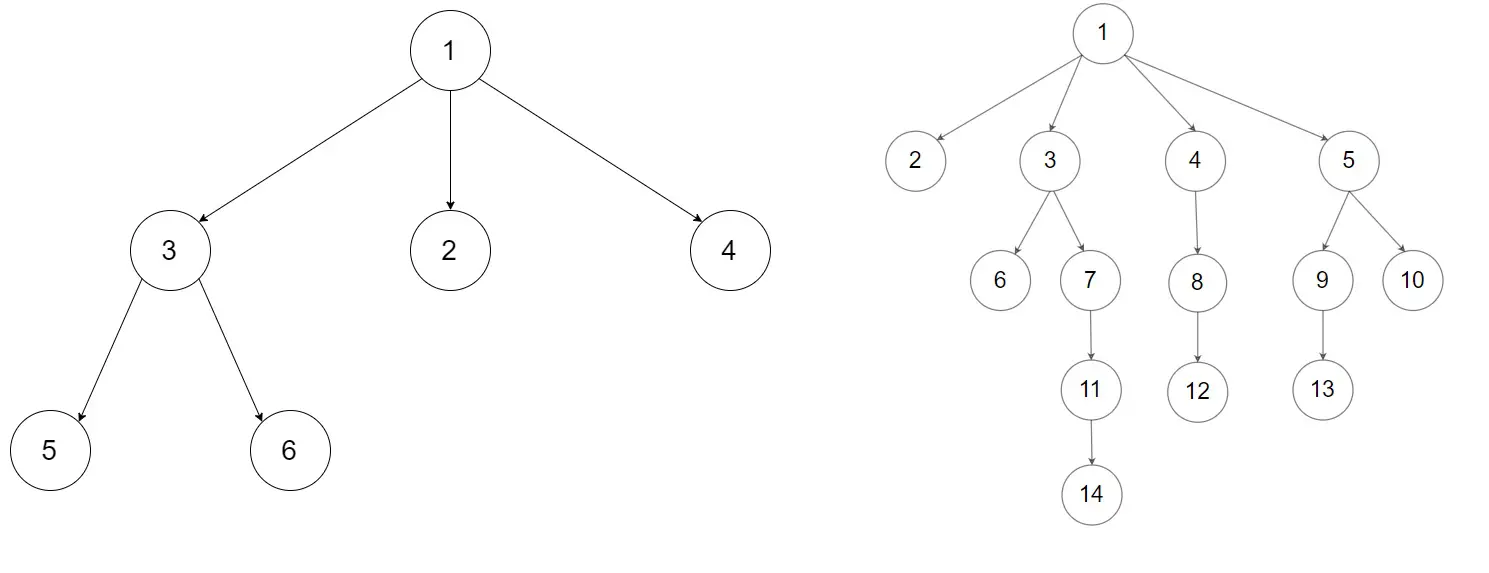
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]Constraints:
The depth of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000.
The total number of nodes is between [0, 10^4].Hints:
Traverse the tree, keep a hashtable with you and create a clone node for each node in the tree.
Start traversing the original tree again and connect each child pointer in the cloned tree the same way as the original tree with the help of the hashtable.
How to Deep Clone a N-ary Tree using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm?
A tree ensures that there is no cycles. A node can only have at most 1 paraent. Thus we can just use recursion to clone each children node of the tree using Depth First Search Algorithm.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* cloneTree(Node* root) { if (!root) return nullptr; Node* newRoot = new Node(root->val); for (const auto &n: root->children) { newRoot->children.push_back(cloneTree(n)); } return newRoot; } }; |
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneTree(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->val);
for (const auto &n: root->children) {
newRoot->children.push_back(cloneTree(n));
}
return newRoot;
}
};Deep Clone a Tree or a Graph using HashMap
If this is a graph – then the above solution might not work. That is because when there are cycles the recursion will not terminate – causing a stack overflow. One way of solving this is to use a hash map to remember the nodes that we already cloned – and return the cloned nodes immediately.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* cloneTree(Node* root) { if (!root) return nullptr; if (memo.find(root) != memo.end()) return memo[root]; Node* newRoot = new Node(root->val); memo[root] = newRoot; for (const auto &n: root->children) { newRoot->children.push_back(cloneTree(n)); } return newRoot; } private: unordered_map<Node*, Node*> memo; }; |
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneTree(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
if (memo.find(root) != memo.end()) return memo[root];
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->val);
memo[root] = newRoot;
for (const auto &n: root->children) {
newRoot->children.push_back(cloneTree(n));
}
return newRoot;
}
private:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> memo;
};Similar to Clone (Deep Copy) Binary Tree With Random Pointer using Hash Map and Recursion, we have to put the new node immediately in the hash map before its children nodes are fully recursively cloned.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:留意幸福角 钉扣子作文400字 清明随感作文 论威严的重要性 拥有一颗周全的心作文 我们一起来向笑猫学习——《笑猫日记》读后感 相亲 描写校园春色的作文 钉扣子作文200字 由大山和卵石的对话想起的作文500字
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论