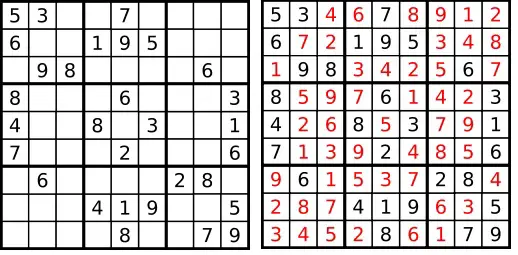
Depth First Search (Backtracking) Algorithm to Solve a Sudoku Ga
- 时间:2020-09-07 12:13:31
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:107 次
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
Each of the the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3×3 sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character ‘.’.sudoku-solver
…and its solution numbers marked in red.Note:
The given board contain only digits 1-9 and the character ‘.’.
You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
The given board size is always 9×9.
Sudoku Solver using Backtracking Algorithm in DFS
The Sudoku can be solved by pure bruteforce algorithm (the complexity is 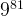 ) . However, the complexity is enormous and can’t be solved practically.
) . However, the complexity is enormous and can’t be solved practically.
By using the 3 rules to abandon search branches and backtracking when solution is invalid – this reduce the complexity to roughly 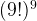 for a standard backtracking algorithm (There are 9! possibilities for 9×9 box and there are 9 of them in permutation).
for a standard backtracking algorithm (There are 9! possibilities for 9×9 box and there are 9 of them in permutation).
We can use three sets – rows, columns, and boxes to remember the digits that have been placed in 9 rows, 9 columns and 9 boxes.
For Depth First Search Algorithm, we try to place next valid number and recursively into next position, and we need to reset to its previous state.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | class Solution { public: void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { for (int r = 0; r < 9; ++ r) { for (int c = 0; c < 9; ++ c) { if (board[r][c] != '.') { int x = board[r][c] - '0'; cols[c].insert(x); rows[r].insert(x); box[r/3][c/3].insert(x); } } } dfs(board, 0, 0); } private: unordered_set<int> cols[9]; unordered_set<int> rows[9]; unordered_set<int> box[3][3]; bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int r, int c) { if (c == 9) { r ++; c = 0; } if (r == 9) { return true; } if (board[r][c] != '.') { return dfs(board, r, c + 1); } for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++ i) { if (check(i, r, c)) { board[r][c] = (char)(48 + i); cols[c].insert(i); rows[r].insert(i); box[r/3][c/3].insert(i); if (dfs(board, r, c + 1)) { return true; } board[r][c] = '.'; cols[c].erase(i); rows[r].erase(i); box[r/3][c/3].erase(i); } } return false; } bool check(int x, int r, int c) { return (cols[c].count(x) == 0) && (rows[r].count(x) == 0) && (box[r/3][c/3].count(x) == 0); } }; |
class Solution {
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
for (int r = 0; r < 9; ++ r) {
for (int c = 0; c < 9; ++ c) {
if (board[r][c] != '.') {
int x = board[r][c] - '0';
cols[c].insert(x);
rows[r].insert(x);
box[r/3][c/3].insert(x);
}
}
}
dfs(board, 0, 0);
}
private:
unordered_set<int> cols[9];
unordered_set<int> rows[9];
unordered_set<int> box[3][3];
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int r, int c) {
if (c == 9) {
r ++;
c = 0;
}
if (r == 9) {
return true;
}
if (board[r][c] != '.') {
return dfs(board, r, c + 1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++ i) {
if (check(i, r, c)) {
board[r][c] = (char)(48 + i);
cols[c].insert(i);
rows[r].insert(i);
box[r/3][c/3].insert(i);
if (dfs(board, r, c + 1)) {
return true;
}
board[r][c] = '.';
cols[c].erase(i);
rows[r].erase(i);
box[r/3][c/3].erase(i);
}
}
return false;
}
bool check(int x, int r, int c) {
return (cols[c].count(x) == 0) && (rows[r].count(x) == 0)
&& (box[r/3][c/3].count(x) == 0);
}
};To check if a Sudoku is valid, we can use this: How to Check Valid Sudoku in C/C++?
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:对大豆制品存在的一些认识误区 食品安全:广州镉超标大米事件追踪 味精的食用安全性及合适用量问题 食品安全问题并不是食品添加剂的错 温州苍南黑作坊两年产千吨剧毒湿米面 食药监总局提醒注意保健食品五大陷阱 对儿童健康成长有益的六大食物 健康养生:七种常见的黑色滋补食物 竹炭食品排毒就是一个忽悠人的概念 中华人民共和国食品安全法(全文)
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论